Decorated with colourful frescos, the snack bar was unearthed back in 2020 in Regio V, the north-eastern sector of Pompeii which spans some 54 hectares.
Archaeologists believed that, in its heyday, the thermopolium would have served the ancient city’s poorer residents, offering such foods as duck, paella and snails.
The diners would rarely have had a kitchen in their own residences, forcing them to visit such eateries instead.
Pompeii and many of its residents were famously submerged beneath pyroclastic flows of searing gas and volcanic matter following the eruption of Mount Vesuvius.
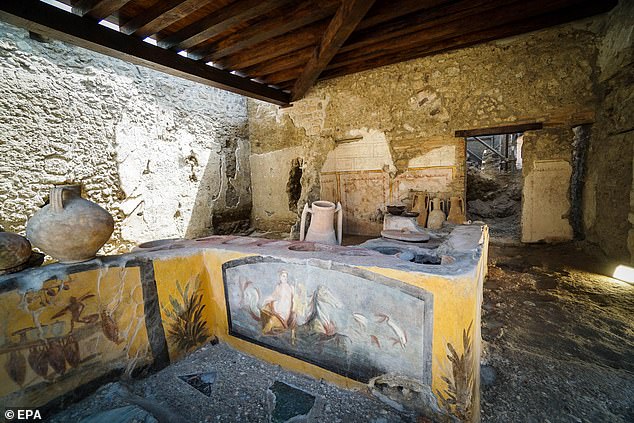

The remains of an ancient fast food joint — or ‘thermopolium’ (pictured) — that was buried in volcanic ash in the Roman city of Pompeii back in 79 AD has opened to tourists
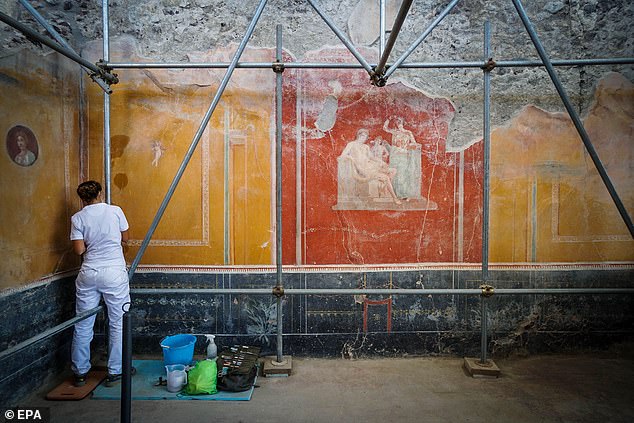

Decorated with colourful frescos (as pictured), the snack bar was unearthed back in 2020 in Regio V, the north-eastern sector of Pompeii which spans some 54 hectares
‘We know what they were eating that day,’ said the former Pompeii Archaeological Park chief, Massimo Osanna, back in 2020, when the thermopolium was first exposed during work to preserve the fragile ruins of the buried city.
Painstaking excavations revealed a multi-sided serving counter with wide holes in its top surface that held deep vessels for hot foods, much like might be seen in present day buffet and salad bars.
In one container, archaeologists found a fragment from a duck’s bone, while other contained the remains of various animals the Romans would have eaten, including fish, goats, pigs and snails.
The researchers have also found nine amphorae — tall ceramic jars used in ancient times to store food and drink — along with a couple of flasks, a bronze ladle and a ceramic-based oil container.
One jug was found to contain traces of ground fava beans, which Romans would add to wine in order to improve its flavour and lighten its colour.
Patrons of the thermopolium would have been greeted with vibrant decorations, with ornate mosaic floors and interior walls that were painted in yellow and orange with various frescos, which also adorned the zig-zag shaped serving counter.
One of these featured a sea nymph — or ‘nereid’ — riding a horse through the waves, while another, perhaps hinting at the food on the menu, depicted two upside-down mallards and a rooster with a plumage vividly painted in so-called ‘Pompeiian red’.
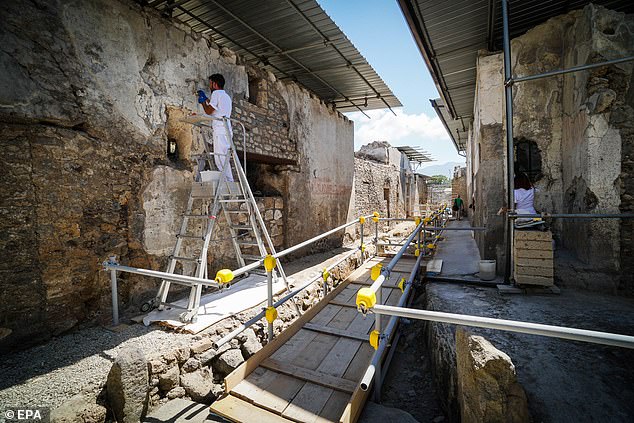

According to Professor Osanna, the thermopolium had a good location in the city, standing as it did on the edge of a square with a fountain. Another snack bar has also been found in the same area. Pictured: archaeologists work to conserve the outer walls of the thermopolium
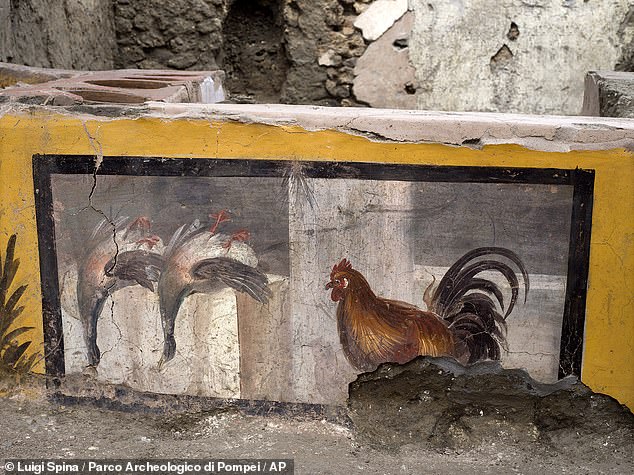

Archaeologists believed that, in its heyday, the thermopolium would have served the ancient city’s poorer residents, offering such foods as duck, paella and snails. Pictured: a fresco on the snack bar’s serving counter depicts two upside-down ducks and rooster
‘The painted images represent, at least in part, the foods and beverages effectively sold inside,’ explained Pompeii staff anthropologist Valeria Amoretti.
Another fresco, meanwhile, featured a dog on a leash. This wasn’t the only pooch-themed discovery in the remains of the thermopolium, however, with archaeologists also unearthing the complete skeleton of an adult canine.
Unlike the big, muscular dog depicted on the counter, however, this one was a small dog. It would have only stood at around 8–10 inches (20–25 cm) at the shoulder and represents something of a rare find from a Roman site.
The discovery of such a small pet, Dr Amoretti explained, attests to the practice of ‘selective breeding in the Roman epoch to obtain this result.’
Human remains were also found in the thermopolium — one of a man who, based on the nails and pieces of wood found under his body, was likely lying on some kind of bed at the time when the aftermath of Vesuvius’ eruption killed him.
Other bones were also found within one of the vessels of the serving counter, and researchers think they may have been placed there when the site was disturbed in the 17th century by diggers looking for valuables.
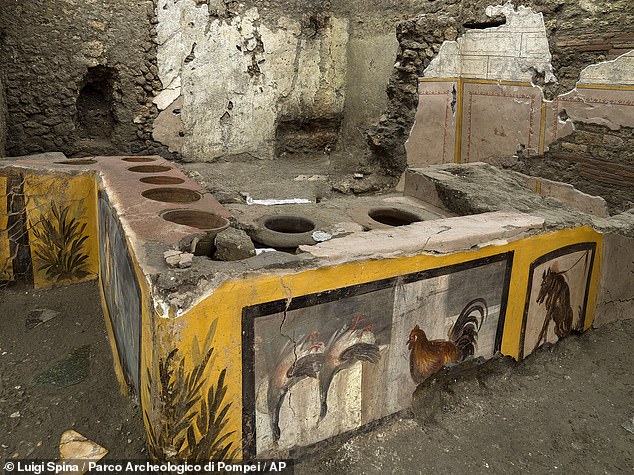

Painstaking excavations in the ancient snack bar revealed a multi-sided serving counter (pictured) with wide holes in its top surface that held deep vessels for hot foods, much like might be seen in present day buffet and salad bars
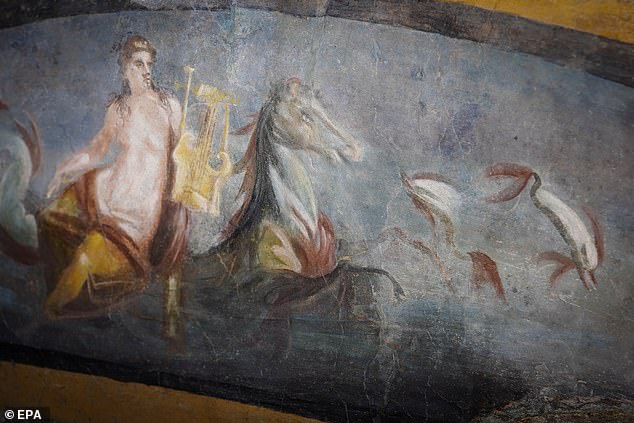

One fresco on the thermopolium counter featured a sea nymph — or ‘nereid’ — riding a horse through the waves (pictured), while another depicted two upside-down mallards and a rooster with a plumage vividly painted in ‘Pompeiian red’
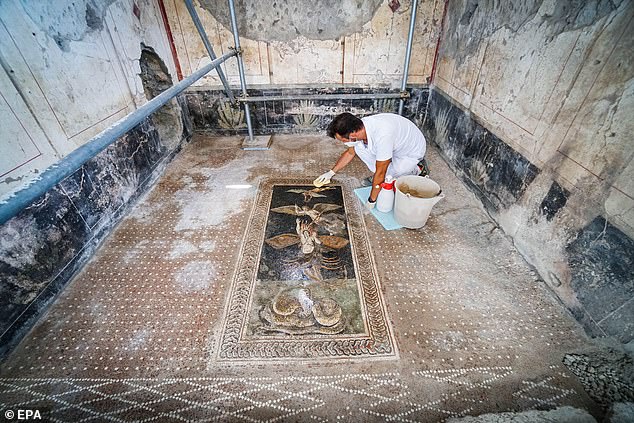

‘We know what they were eating that day,’ said the former Pompeii Archaeological Park chief, Massimo Osanna, back in 2019, when the thermopolium was first exposed during work to preserve the fragile ruins of the buried city. Pictured: a worker cleans a mosaic on the floor of the thermopolium, which has recently opened to the public
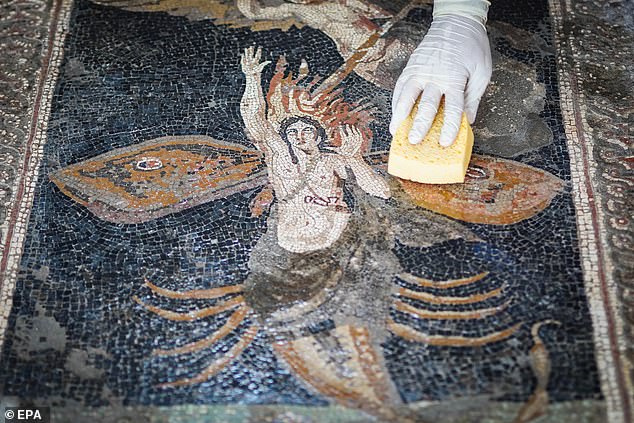

In the thermopolium, archaeologist found nine amphorae — tall ceramic jars used in ancient times to store food and drink — along with a couple of flasks, a bronze ladle and a ceramic-based oil container. Pictured: worker cleans a detailed mosaic on the floor of the snack bar
According to Professor Osanna, the thermopolium had a good location in the city, standing as it did on the edge of a square with a fountain.
Another snack bar has also been found in the same area. (In total, 12 thermophobia have been found in the city.)
Regio V, the sector of the city in which the recently opened thermopolium is located, has been the focus of the most intensive excavation and restoration efforts in Pompeii ever since the 1960s.
Visitors to the thermopolium will also be able to see two large villas in the area — the ‘Casa di Orione’ and ‘Casa del Giardino’ — which are in the process of being restored.