A unique, full-length mummy shroud, which is over 2,000 years old, has been discovered in a museum collection.
The shroud, which dates to approximately 9 BC, was discovered in a brown paper parcel by curators looking through the National Museum of Scotland’s ancient Egyptian collections.
The incredible artefact will finally go on display for the public at ‘The Tomb: Ancient Egyptian Burial’ exhibition in Edinburgh opening on 31 March.
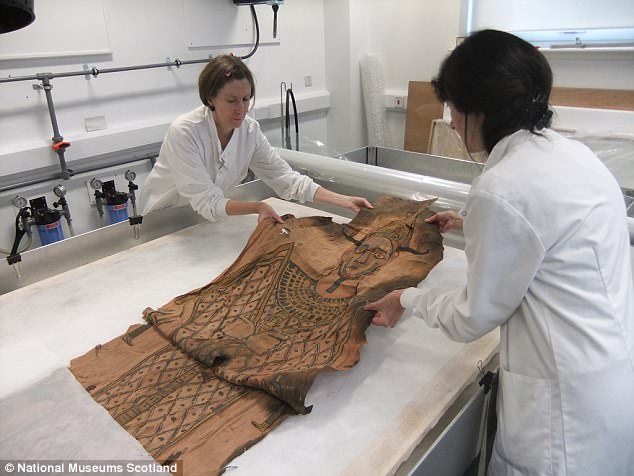

The 2,000-year-old shroud was found in the National Museum of Scotland’s ancient Egyptian collections. It will go on display for the first time at ‘The Tomb: Ancient Egyptian Burial’ exhibition, which opens on 31 March
The shroud was discovered in brown paper, along with an 80-year-old note from a previous curator.
A hieroglyphic inscription on the shroud revealed the identity of the owner to be the previously unknown son of the Roman-era high-official Montsuef and his wife Tanuat.
Due to the fragility of the ancient textile, conservators gently humidified it so that the fibres would become less dry and brittle as they removed it from its brown parcel.
This allowed them to carefully unfold the shroud – a process which took almost 24 hours.
Dr Margaret Maitland, Senior Curator of Ancient Mediterranean collections who found the package said: ‘To discover an object of this importance in our collections, and in such good condition, is a curator’s dream.
‘Before we were able to unfold the textile, tantalising glimpses of colourful painted details suggested that it might be a mummy shroud, but none of us could have imagined the remarkable figure that would greet us when we were finally able to unroll it.
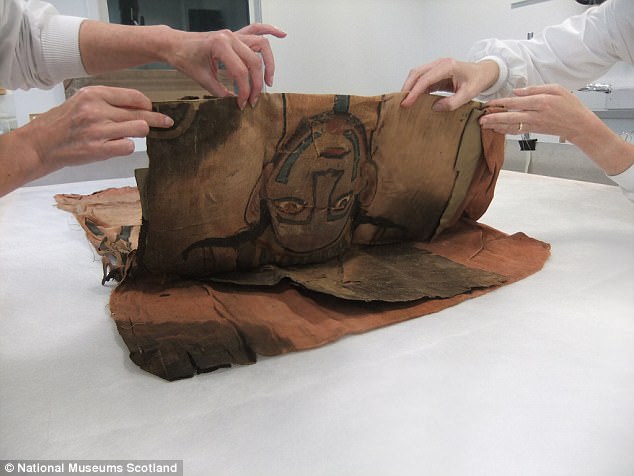

A hieroglyphic inscription on the shroud revealed the identity of the owner to be the previously unknown son of the Roman-era high-official Montsuef and his wife Tanuat
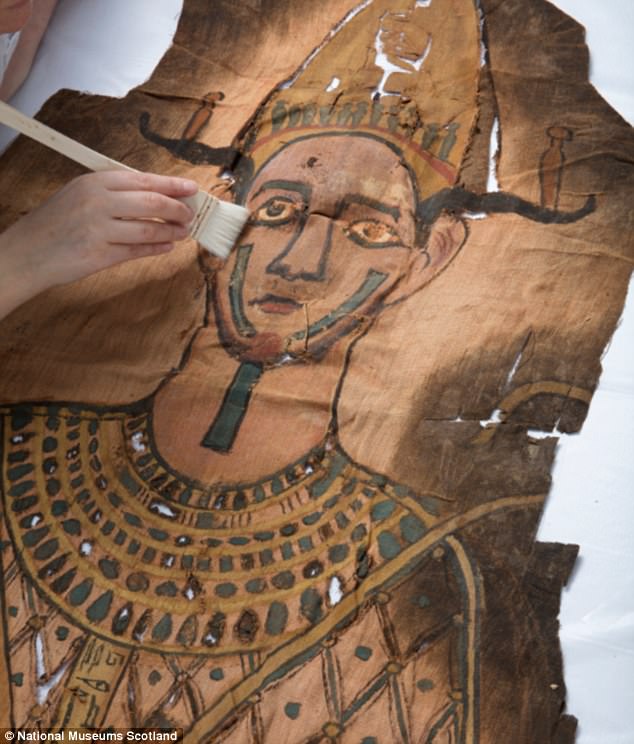

The full-length, painted linen shroud is unique, with very few parallels from its period. It was made in approximately 9 BC and had been sitting in storage since the 1940s
‘The shroud is a very rare object in superb condition and is executed in a highly unusual artistic style, suggestive of Roman period Egyptian art, yet still very distinctive.’
In ancient Egypt, following mummification, a shroud was commonly wrapped around the body before it was placed in a coffin.
In Roman-era Egypt, shrouds became increasingly important as the use of coffins became rarer.
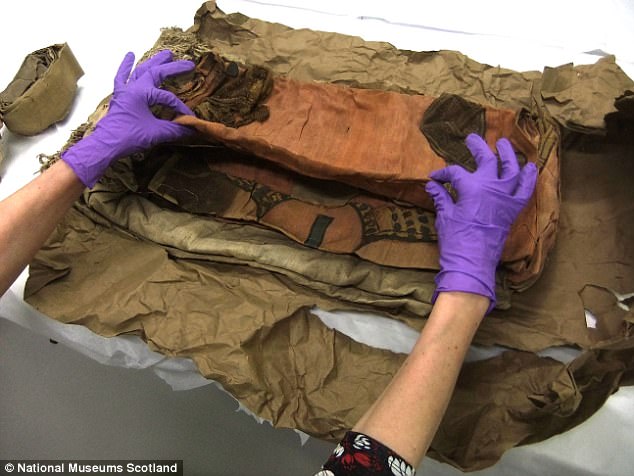

Due to the fragility of the ancient textile, conservators gently humidified it so that the fibres would become less dry and brittle as they removed it from its brown parcel

The shroud comes from a Roman-era burial in a tomb originally built around 1290 BC opposite the great city of Thebes (modern-day Luxor). It depicts the deceased as the god Osiris
This full-length, painted linen shroud is unique, with very few parallels from its period. It depicts the deceased as the god Osiris.

Because of its owner’s direct relationship to Montsuef and Tanuat, whose deaths were recorded to have occurred in 9 BC, it is possible to date the shroud relatively precisely, which is extraordinary for such an ancient artefact.
The shroud comes from a Roman-era burial in a tomb originally built around 1290 BC opposite the great city of Thebes (modern-day Luxor).
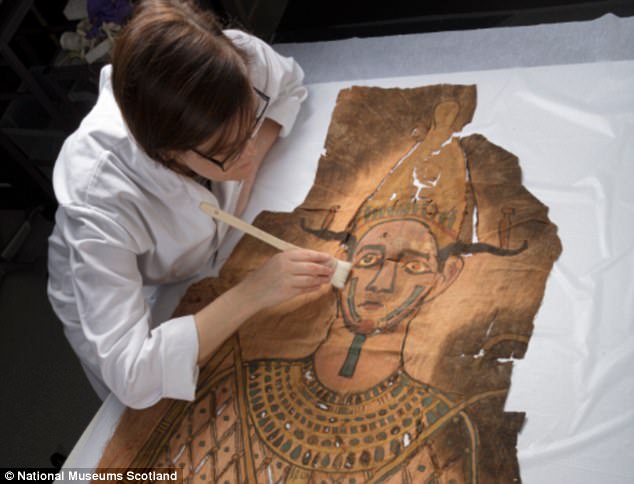

In Roman-era Egypt, shrouds became increasingly important as the use of coffins became rarer. The package had been stored since the mid-1940s

Because of its owner’s direct relationship to Montsuef and Tanuat, whose deaths were recorded to have occurred in 9 BC, it is possible to date the shroud relatively precisely, which is extraordinary for such an ancient artefact

First built for a chief of police and his wife, it was looted and reused several times, before being sealed in the early 1st century AD.
It was undisturbed until its excavation in the 19th century when a collection of beautiful objects from various eras was discovered.
The shroud is one of a number of objects from this tomb which are in the National Museums Scotland’s collections.
The exhibition will tell the story of this tomb across 1,000 years of use.